Introduction to Loguytren Problems
Loguytren problems—more formally known in the medical world as Dupuytren’s contracture—are a lesser-known but significantly life-impacting condition that affects the hand. Characterized by the thickening and shortening of the fascia (a layer of connective tissue under the skin in the palm), it eventually pulls one or more fingers into a permanently bent position. Though painless in most cases, it can severely impact a person’s ability to perform everyday tasks like grasping objects, shaking hands, or writing. For those suffering from loguytren problems, early detection and appropriate treatment can make a substantial difference in maintaining hand function and quality of life.
Despite being around for centuries, loguytren problems often go undiagnosed or ignored in their early stages. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the root causes of the condition, how to identify early symptoms, who’s at risk, the latest diagnostic methods, and the best treatment strategies—including both non-invasive and surgical solutions.
What Exactly Are Loguytren Problems?
Loguytren problems refer to a progressive fibrosis of the palmar fascia that leads to the development of nodules, cords, and eventually, finger contractures. The condition is most common in middle-aged or older adults, with men being significantly more affected than women. Often starting in one hand, it can progress to both, and while the ring and little fingers are most commonly involved, the thumb and index fingers may also be affected in advanced cases.
Unlike arthritis or tendinitis, loguytren problems are not related to inflammation or joint degradation. Instead, the issue lies in the skin and underlying fascia, which becomes abnormally thick and forms tight bands. These cords act like ropes, pulling the fingers inward over time. The resulting flexion deformity can be mild or severe depending on how early it is diagnosed and treated.
Understanding the Causes Behind Loguytren Problems
Although medical science has yet to pinpoint a single cause for loguytren problems, researchers believe the condition is influenced by a combination of genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors. Here are some of the most widely recognized causes and contributing elements:
- Genetics: A strong hereditary link has been identified, particularly among individuals of Northern European descent. If a parent or close relative has had the condition, you are more likely to develop it.
- Age and Gender: Loguytren problems are most common in men over the age of 40. The likelihood increases with age, and men are up to 10 times more likely than women to develop severe contractures.
- Chronic Conditions: People with diabetes, epilepsy, or liver disease have a higher incidence of loguytren problems. It’s believed that changes in connective tissue metabolism may play a role.
- Lifestyle Habits: Heavy alcohol use and smoking are associated with a higher risk, likely due to poor blood flow and tissue damage over time.
- Trauma and Occupational Use: While not a direct cause, repetitive hand trauma or intense use of the hands may accelerate the condition in genetically predisposed individuals.
Understanding the causes allows medical professionals to determine the best course of action for prevention and early intervention.
Recognizing the Early Symptoms of Loguytren Problems
Catching loguytren problems in their early stages can significantly improve treatment outcomes. Symptoms usually develop slowly and painlessly, often going unnoticed until functional impairment begins. Key symptoms include:
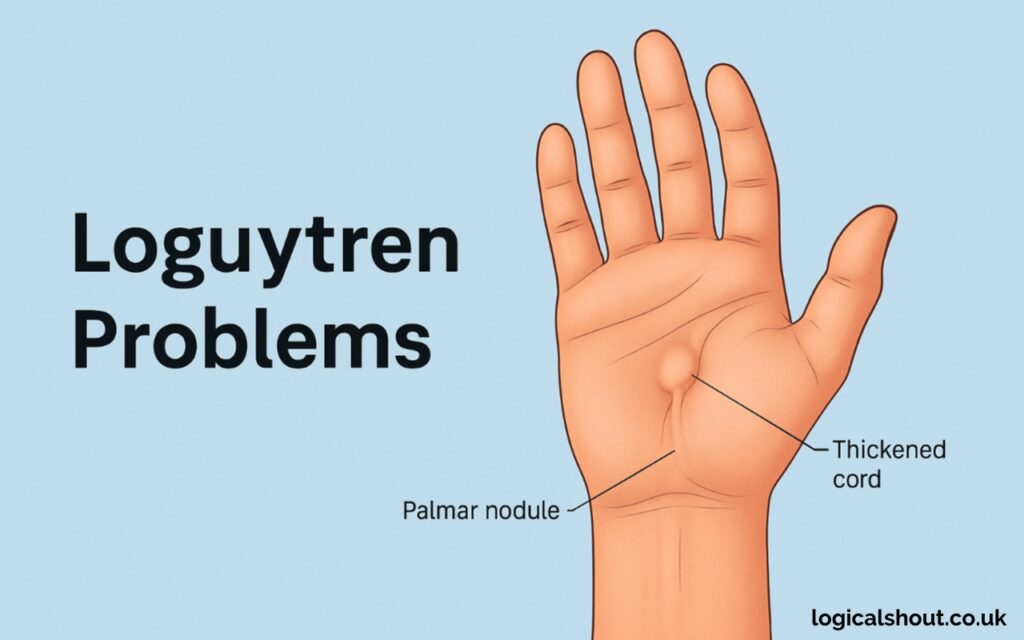
- Palmar Nodules: The first sign is typically a small lump in the palm, which may feel tender initially but usually becomes painless.
- Formation of Cords: Over time, nodules can develop into thickened cords of tissue beneath the skin, which start to pull the fingers inward.
- Finger Contractures: The most visible and debilitating symptom is when one or more fingers become permanently bent toward the palm. This can make it difficult or impossible to lay the hand flat on a surface.
- Skin Changes: The skin over the nodules may appear puckered or dimpled, a sign of fascia tightening beneath the surface.
Not everyone will progress to the stage of significant contracture. However, even minimal changes in hand flexibility should prompt a medical evaluation to assess the presence of loguytren problems.
Who Is Most at Risk of Developing Loguytren Problems?
While anyone can potentially develop loguytren problems, some demographics are more at risk:
- Men Over 40: As mentioned, age and gender are major factors. Men in their 50s and 60s are most commonly affected.
- People of Northern European Descent: Known as the “Viking disease,” this condition is particularly prevalent among those with Scandinavian or Celtic ancestry.
- Family History: If loguytren problems run in the family, your chances of developing them increase significantly.
- Chronic Disease Patients: Individuals with diabetes, epilepsy, and thyroid issues should be especially vigilant.
- Lifestyle-Related Risk: Smokers and those who consume alcohol heavily may be at a higher risk due to vascular and tissue damage.
Awareness of these risk factors can aid in early detection and preventive care.
Diagnosis: How Loguytren Problems Are Identified
Diagnosing loguytren problems usually doesn’t require complex medical tests. A clinical evaluation by a hand specialist is often sufficient. During your appointment, the doctor will:
- Conduct a Physical Examination: The physician will look for nodules and cords in the palm and test the flexibility of your fingers.
- Perform the Tabletop Test: You’ll be asked to place your hand flat on a table. If you cannot do this due to finger flexion, it’s a strong indicator of a contracture.
- Assess Functional Impairment: The doctor will evaluate how much the condition impacts daily activities and range of motion.
- Use Imaging if Necessary: In complex cases or pre-surgical planning, ultrasound or MRI may be used to map the extent of the tissue involvement.
Prompt diagnosis is crucial to stopping the progression of loguytren problems and restoring functionality through treatment.
Non-Surgical Treatment Options for Loguytren Problems
If detected early, non-invasive treatments may be effective in managing the symptoms of loguytren problems. Here are several options:
- Watchful Waiting: In mild cases without hand dysfunction, doctors may recommend monitoring without intervention.
- Steroid Injections: Corticosteroids can help reduce inflammation and nodule size in the early stages.
- Enzyme Therapy (Collagenase): This involves injecting collagenase clostridium histolyticum into the cords to dissolve them. This method, marketed as XIAFLEX®, is FDA-approved and can improve finger extension without surgery.
- Physical Therapy: While not a cure, therapy can help maintain hand mobility and slow progression through specific stretches and strengthening exercises.
These options are best suited for individuals in the early or moderate stages of loguytren problems.
Surgical Interventions: When and How They’re Performed
For those with advanced contractures or significant functional limitations, surgical treatment is often the best solution. Common procedures include:
- Fasciotomy: A less invasive procedure where the contracted cord is cut but not removed. This can be done using a needle or scalpel.
- Subtotal Palmar Fasciectomy: This surgery removes the thickened cords and tissue. It offers longer-lasting results but requires a longer recovery time.
- Dermofasciectomy: In cases where the disease is likely to recur, the affected fascia and overlying skin are removed and replaced with a skin graft.
Post-surgery rehabilitation is essential and includes physical therapy, splinting, and regular follow-ups to prevent recurrence.
Living with Loguytren Problems: Managing the Daily Impact
Adapting to life with loguytren problems means learning new strategies to maintain independence. Here are some helpful tips:
- Use Assistive Tools: Devices like adaptive grips or ergonomic handles can reduce strain.
- Modify Daily Tasks: Activities such as writing, cooking, and typing may require small adjustments or the use of the unaffected hand.
- Stay Active: Engage in hand-strengthening and stretching exercises as recommended by therapists.
- Join Support Groups: Connecting with others facing similar challenges can provide emotional support and practical advice.
With the right approach, individuals with loguytren problems can maintain a high quality of life.
Read More: Food Jalbiteblog Trend Justalittlebite: Your Ultimate Source for Trending Recipes
Conclusion: The Importance of Early Detection and Comprehensive Care
Loguytren problems may start as a subtle nuisance, but without proper care, they can escalate into a severe disability affecting everyday life. Fortunately, modern medicine offers a range of treatment options—both non-invasive and surgical—that can dramatically improve hand function. The key lies in early detection, appropriate medical consultation, and proactive treatment. If you or a loved one notices signs of this condition, don’t wait. Seek expert advice and start managing loguytren problems before they take a deeper hold.